C++ Case Study.
This case study is a program that can be used in a small library to include new books in the library, to check out books to people, and to return them. As this program is a practice in the use of linked lists, almost everything is implemented in terms of such lists. But to make the program more interesting, it uses linked lists of linked lists that also contain cross-references (see Figure 3.26). First, there could be a list including all authors of all books in the library. However, searching through such a list can be time-consuming, so the search can be sped up by choosing at least one of the two following strategies: ■ The list can be ordered alphabetically, and the search can be interrupted if we find the name, if we encounter an author’s name greater than the one we are searching for, or if we reach the end of list. ■ We can use an array of pointers to the author structures indexed with letters; each slot of the array points to the linked list of authors whose names start w...
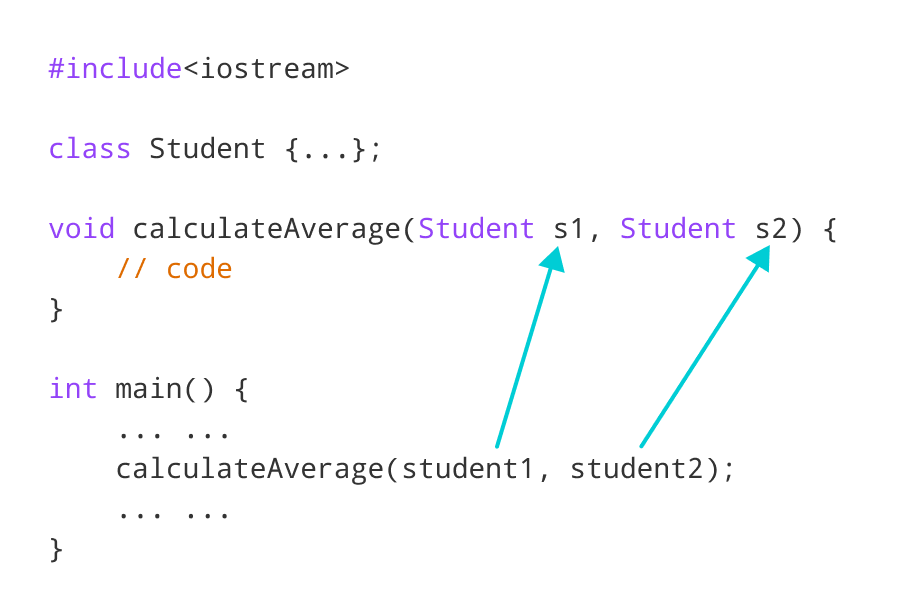
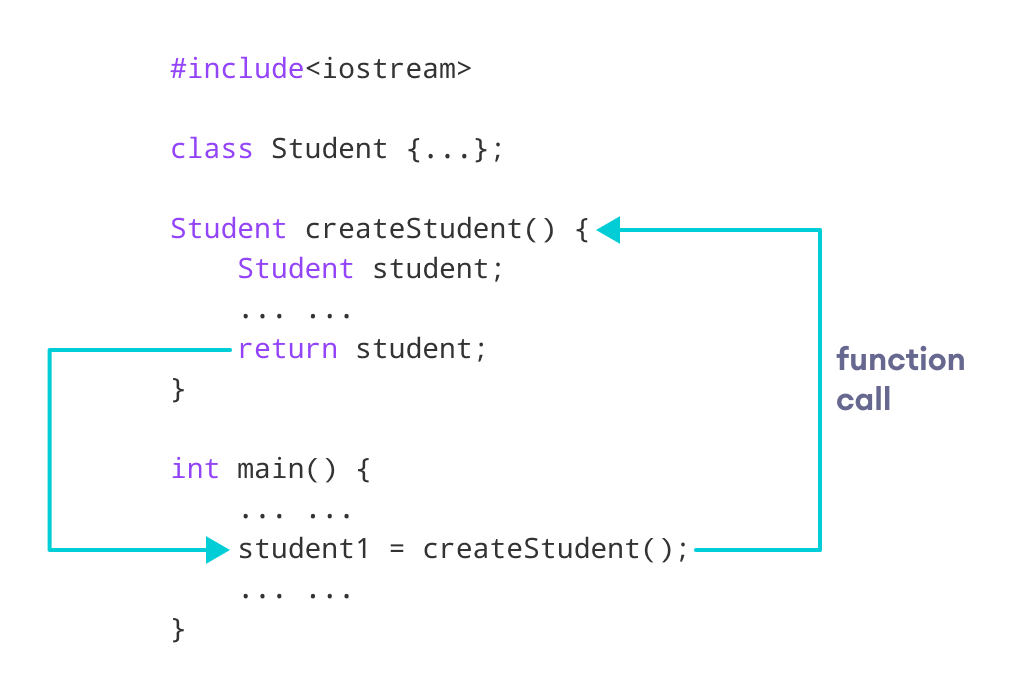
Comments
Post a Comment